Authors
Jennifer Kreie & John Pendley
Abstract
In recent years, spreadsheets have taken on a role far more important than they had in the pre-computer days: shaping business strategies and being used increasingly for ongoing projects by many different people who need to go in and out of a file, to add material and even to customize the output for their specific needs.
This presents a new challenge for the spreadsheet developer, who must design the file so it cannot be accidentally altered by an inexperienced user.
Here are steps to ensure safe spreadsheet design:
- Decide what you want the spreadsheet to do. List the data to be used and the output you want. Then identify the calculations needed to produce that output.
- Lay out the spreadsheet structure and, if necessary, divide it into logically related sections, such as identification, description, model, documentation and macros.
- Create the spreadsheet. Familiarize yourself with the use of absolute and relative cell references. Its proper use is critical to the success of the input, calculation and output areas.
- Test the spreadsheet by selecting a set of test values, and then test the results independently of your spreadsheet.
Sample
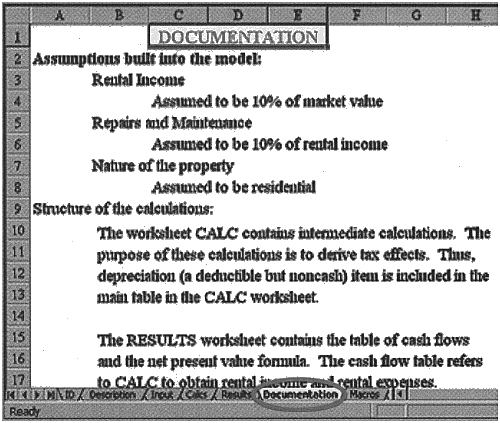
The documentation module includes detailed explanations about the application. It may contain specific clarifications such as data format, identity of protected cells, special printing instructions or any other important information the developer wants to include.
Publication
1998, Journal of Accountancy, Volume 186, Number 5, November, pages 31-34
