Authors
Ruiqing Zhang, Chang Xu, Shing-Chi Cheung, Ping Yu, Xiaoxing Ma, & Jian Lu
Abstract
While spreadsheets are widely used, they have been found to be error-prone. Various techniques have been proposed to detect anomalies in spreadsheets, with varying scopes and effectiveness. Nevertheless, there is no empirical study comparing these techniques' practical usefulness and effectiveness.
In this work, we conducted a large-scale empirical study of three state-of-the-art techniques on their effectiveness in detecting spreadsheet anomalies. Our study focused on the precision, recall rate, efficiency and scope. We found that one technique outperforms the other two in precision and recall rate of spreadsheet anomaly detection.
Efficiency of the three techniques is acceptable for most spreadsheets, but they may not be scalable to large spreadsheets with complex formulas. Besides, they have different scopes for detecting different spreadsheet anomalies, thus complementing to each other.
We also discussed limitations of these three techniques. Based on our findings, we give suggestions for future spreadsheet research.
Sample
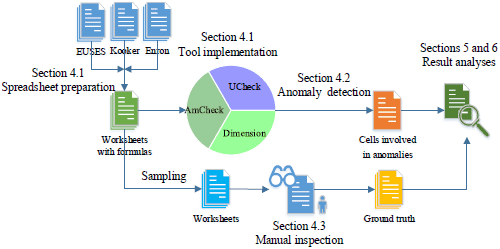
We first preprocessed the three corpora and implemented interfaces for manipulating the three tools (techniques).
Then we used the adapted tools to detect anomalies in worksheets and recorded cells and worksheets involved in anomalies.
At last, we inspected sampled worksheets for the ground truth and analyzed experimental results.
Publication
2017, Journal of Systems and Software, Volume 126, pages 87-100
Full article
How effectively can spreadsheet anomalies be detected: An empirical study
