Authors
Birgit Hofer, Andrea Hofler, & Franz Wotawa
Abstract
Spreadsheets are the most prominent example of end-user programing, but they unfortunately are often erroneous, and thus, they compute wrong values.
Localizing the true cause of such an observed misbehavior can be cumbersome and frustrating especially for large spreadsheets. Therefore, supporting techniques and tools for fault localization are highly required.
Model-based software debugging (MBSD) is a well-known technique for fault localization in software written in imperative and object-oriented programing languages like C, C++, and Java.
In this paper, we explain how to use MBSD for fault localization in spreadsheets and compare three types of models for MBSD, namely the value-based model (VBM), the dependency based model (DBM), and an improved version of the DBM.
Whereas the VBM computes the lowest number of diagnoses, both DBMs convince by their low computational complexity. Hence, a combination of these two types of models is desired, and we present a solution that combines value-based and DBM in this paper.
Moreover, we discuss a detailed evaluation of the models and the combined approach, which indicates that the combined approach computes the same number of diagnoses like the VBMs while requiring less computation time. Hence, the proposed approach is more appropriate to be used in tools for fault localization in spreadsheets.
Sample
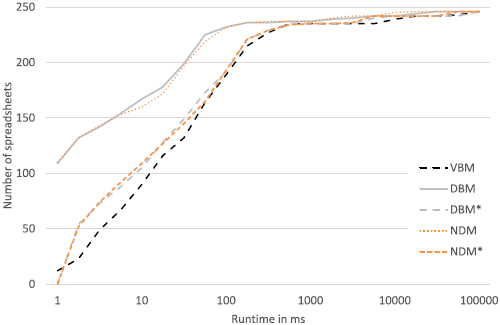
The diagnosis partitioning approach requires more runtime than the basic DBMs, but less time than the VBM — the median runtime is 30% lower — while still offering the same diagnostic accuracy.
Publication
2017, IEEE Transactions on reliability, Volume 66, Number 1, March, pages 38-53
Full article
Combining models for improved fault localization in spreadsheets
